Unveiling the Latest Periodic Table of Elements: Exploring Structure, Uses, and Beyond
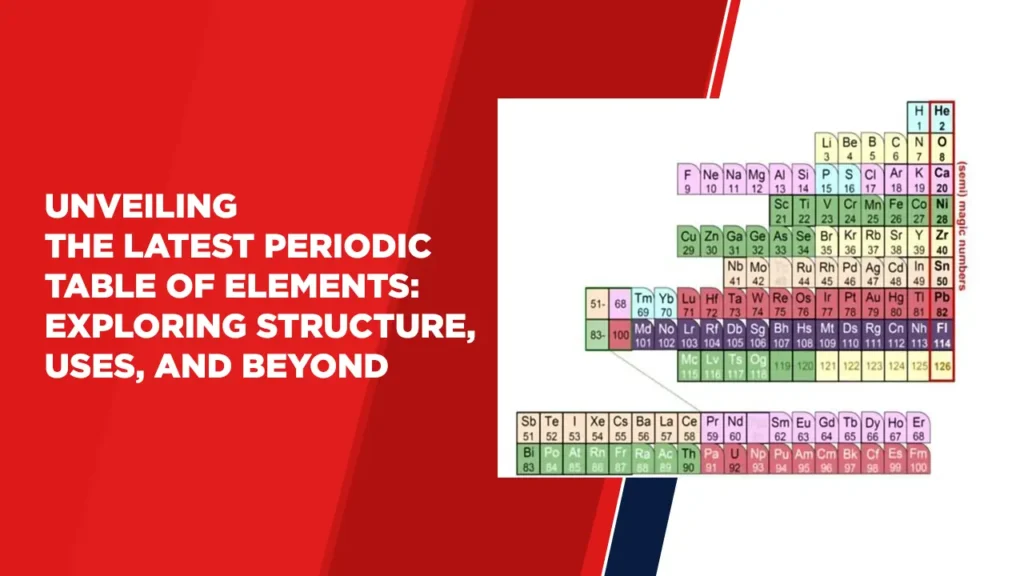
The periodic table of elements, a cornerstone of modern chemistry, has recently undergone intriguing updates. This table organizes the building blocks of matter, offering insight into the fundamental properties and behaviors of elements. It presents a symphony of elements, each characterized by atomic number, mass, and unique properties that hold the key to our understanding of the natural world.
Structure and Significance:
The latest periodic table boasts an elegant arrangement of elements based on atomic number, a value that defines the number of protons in an atom’s nucleus. This arrangement reflects the periodicity of elemental properties, with columns representing groups and rows signifying periods. As we traverse across a period, atomic numbers rise, unveiling new electron shells. Meanwhile, moving down a group introduces analogous valence electron configurations, leading to similar chemical behavior.
Atomic Number and Mass:
The atomic number, alongside atomic mass, is a cornerstone of the periodic table’s organization. The atomic mass of an element’s isotopes contributes to the weighted average that graces the table. Elements are classified as heavy or light based on this average, with the distinction often having profound implications for an element’s stability and reactivity.
Element Symbols and Uses:
Each element is denoted by a symbol derived from its name, often in Latin or its first few letters. These symbols provide a succinct way to represent elements and facilitate universal communication in the world of science.
The periodic table is more than just a collection of data; it holds practical significance. Elements find applications in countless industries and fields. Hydrogen, the lightest element, powers fuel cells and is crucial for the production of ammonia. Silicon, a cornerstone of electronics, underpins the modern digital age. Heavy elements, often forged in the heart of stars, play roles in nuclear reactors, medical imaging, and cutting-edge research.
Exploring Heavy Elements:
Heavy elements, found in the latter portions of the periodic table, captivate scientists and researchers. Many of these elements are synthesized in laboratories, often for fractions of a second, offering glimpses into uncharted territory. Elements like uranium and plutonium have far-reaching consequences in nuclear energy and weaponry, while newer, synthetic elements expand our understanding of the possible forms of matter.
Conclusion:
The periodic table of elements remains a testament to human curiosity and our ceaseless quest to understand the world around us. As we delve into the intricacies of atomic structure, properties, and applications, the periodic table’s latest iterations continue to serve as blueprints for innovation, guiding scientific discoveries that shape our present and future. The table’s rows and columns remind us of the interconnectedness of the elements and their profound influence on our lives, from the most mundane substances to the most advanced technological breakthroughs.