Mathematics, often regarded as the universal language, relies on rules and principles to solve problems accurately. One such fundamental rule is the BODMAS Rule, a mnemonic that helps in determining the order of operations when solving mathematical expressions. BODMAS ensures clarity and consistency in calculations, enabling students and mathematicians to approach complex expressions systematically.
What is the BODMAS Rule?
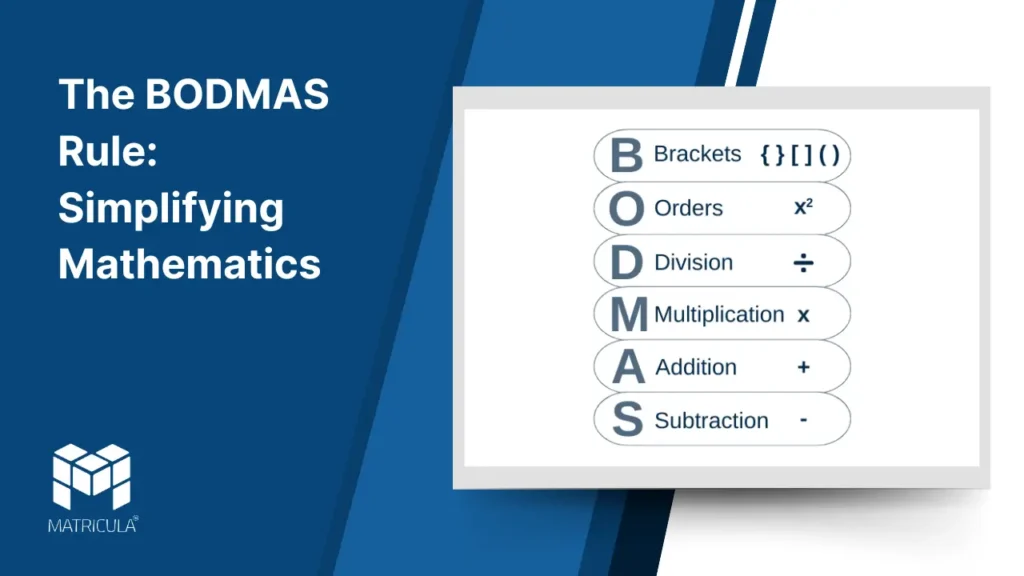
The term BODMAS is an acronym that stands for:
- B: Brackets
- O: Orders (exponents and roots)
- D: Division
- M: Multiplication
- A: Addition
- S: Subtraction
The rule provides a hierarchy of operations, indicating which operation should be performed first in a mathematical expression. By following this sequence, one can resolve ambiguity in equations and arrive at the correct result.
The Order of Operations
Brackets: Solve expressions inside brackets first. These include parentheses (()), square brackets ([]), and curly brackets ({}).
Example: In the expression (3+2)×4, calculate 3+2 first to get 5, and then multiply by 4 to get 20.
Orders: Solve powers (exponents) or roots next.
Example: In 23+4, calculate 23 (which is 8) before adding 4, resulting in 12.
Division and Multiplication: Perform these operations from left to right, whichever comes first.
Example: In 16÷4×2, divide 16 by 4 to get 4, and then multiply by 2 to get 8.
Addition and Subtraction: Finally, handle addition and subtraction, again working from left to right.
Example: In 10−3+2, subtract 3 from 10 to get 7, and then add 2 to get 9.
Why is the BODMAS Rule Important?
Without a consistent order of operations, mathematical expressions can yield multiple answers, leading to confusion and errors. For example, consider the expression 8+4×2:
- Without BODMAS, one might add 8+4 first to get 12, then multiply by 2 for 24.
- Using BODMAS, multiplication is performed first (4×2 = 8), and then addition (8+8 = 16).
Clearly, the BODMAS Rule ensures uniformity and prevents misinterpretation.
Applications of the BODMAS Rule
The BODMAS Rule is used in:
- Arithmetic calculations: Simplifying daily calculations or solving numerical problems.
- Algebra: Managing expressions with variables and constants.
- Programming: Writing algorithms where mathematical expressions need clarity.
- Physics and Engineering: Ensuring accurate results in equations with multiple operations.
Common Misconceptions
A common error is ignoring the left-to-right sequence for division and multiplication or addition and subtraction. For example, in 12÷3, division (12÷3 = 4) must occur first, followed by multiplication (4×2 = 8).