Unveiling the Secrets: Mastering Physics Through Dynamic Speed-Time Graphs
Introduction
Speed-time graphs are invaluable tools for visualizing the motion of objects over time. They offer a comprehensive view of how an object’s motion changes, helping us analyze its acceleration, deceleration, and uniform motion. In this article, we will discuss the key components of a speed-time graph in depth, understanding how they provide insight into an object’s travel through time.
The Basics: Speed vs. Time
At the core of understanding speed-time graphs is the relationship between speed and time. The x-axis of the graph represents time, while the y-axis represents speed. This arrangement allows us to track the motion of an object as it moves over time, capturing the nuances of its motion.
Interpreting the Slope
A fundamental aspect of a speed-time graph is its slope. Slope measures how fast the speed changes over time. In mathematical terms, this is the increase during the race – how much the speed changes (increase) divided by the corresponding change in time (race). Therefore, a steeper slope indicates a more rapid change in speed, which implies significant acceleration or deceleration. On the other hand, a gentle slope symbolizes a more gradual change in speed.
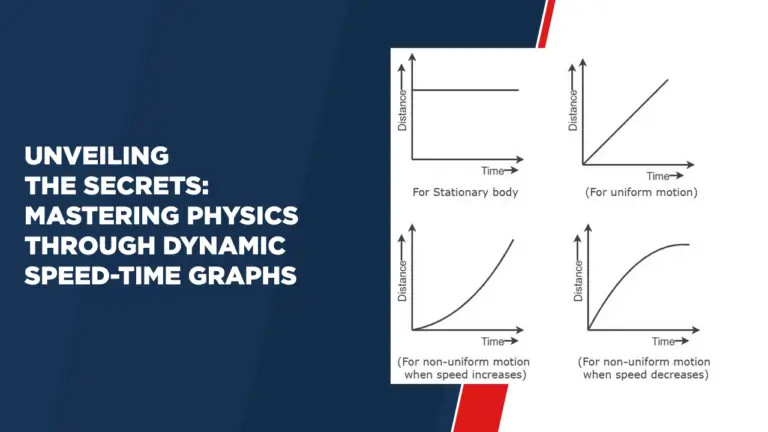
Uniform Motion: A Straight Line
For an object in uniform motion – when its speed remains constant – the speed-time graph takes a different form: a straight horizontal line. This line shows that the speed of the object remains the same throughout its journey. This type of speed is often seen in scenarios such as traveling at a constant velocity on a highway.
Area Under the Graph
The area covered by the speed-time graph has important meaning. It shows the distance covered by the object during the given time interval. This concept arises from the fundamental kinetic equation: distance = speed × time. When the speed is changing, the shape of the graph will create irregular areas, each of which corresponds to a different distance traveled. Calculating these areas helps us understand the total distance covered and different segments of speed during the journey.
Analyzing Acceleration and Deceleration
When a speed-time graph displays an upward sloping curve, it indicates acceleration. This means that the object is gaining momentum with time. Conversely, a downward sloping curve represents recession – slowing down. These curves provide insight into the behavior of an object, showing how its speed changes in response to external forces.
Conclusion
Speed-time graphs are invaluable tools for visualizing the complex interplay between speed and time during the motion of an object. By interpreting the slope, identifying uniform motion, and calculating the area under the graph, we gain an overall understanding of the object’s travel. These graphs provide insight into acceleration, deceleration, and patterns of motion, making them indispensable tools in the world of physics and motion analysis. So, the next time you encounter a motion-time graph, remember the wealth of information it contains about an object’s dynamic travel through time.