Empowering Your Physics Arsenal: Unleashing the Potential of Radius of Gyration
Introduction
In the field of mechanics, the concept of radius of gyration plays an important role in understanding the distribution of mass in rotating objects. This fundamental property provides valuable insight into an object’s ability to resist rotational motion. In this article, we will learn in detail about the meaning of radius of gyration, its formula, unit and its importance in the world of mechanics.
What is Radius of Gyration?
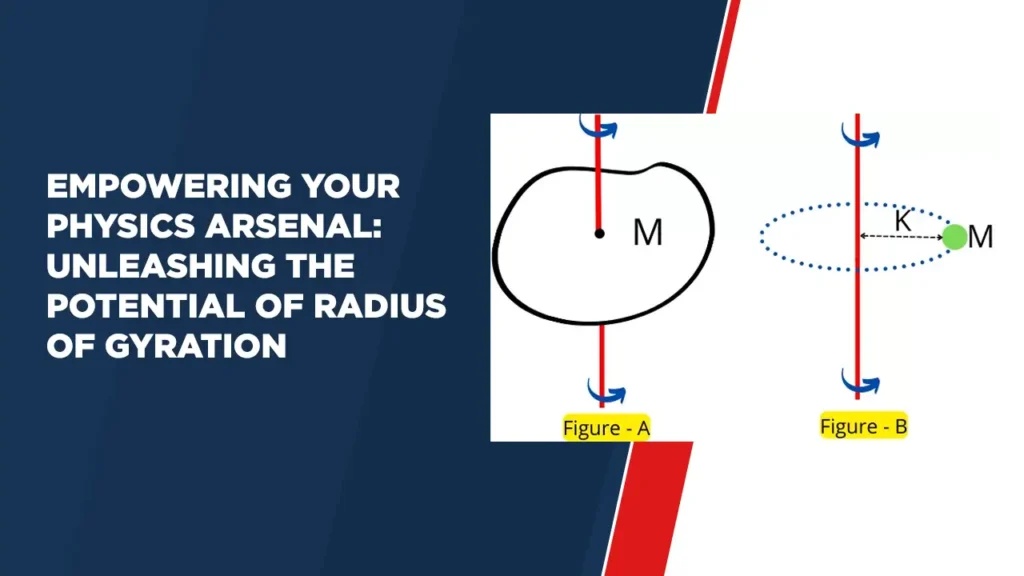
The radius of gyration, often denoted as ‘k’ or ‘r’, is a measure of how an object’s mass is distributed around its axis of rotation. It is defined as the square root of the ratio of the moment of inertia of an object to its mass. Mathematically, the formula for the radius of gyration is given as:
k=I/m
Where:
– k is the radius of gyration
– I is the moment of inertia of the object
– m is the mass of the object
What is the Unit of Radius of Gyration?
The unit of radius of gyration is analogous to the unit system used for moment of inertia and mass. In the International System of Units (SI), moment of inertia is measured in kilograms squared (kg.m2) and mass is measured in kilograms (kg). Consequently, the unit of radius of gyration is also in meter (m).
Why is it Useful to Define Radius of Gyration?
Defining the radius of gyration provides a concise representation of the mass distribution of an object in rotational motion. This provides several practical advantages:
- Simplification of rotational motion:
The radius of gyration simplifies the equations of rotational motion, making them more manageable and applicable to a variety of scenarios.
2. Design and Engineering:
In engineering, understanding the radius of gyration helps in designing structures and mechanisms that need to maintain balance during rotation, such as flywheels and rotating machinery.
3. Sports and fitness:
In sports such as gymnastics and figure skating, athletes use their knowledge of turning radius to control their rotational speed and stability during maneuvers.
4. Astronomy:
The concept of radius of gyration is also applied in astronomy to study the distribution of mass in celestial bodies, influencing their rotational behavior.
Conclusion
Finally, the radius of gyration is an important concept in mechanics, providing valuable insights into rotational motion and mass distribution. Its formula, k=I/m, provides a straightforward method for calculating this parameter. The SI unit of radius of gyration is the metre, which is analogous to the unit of moment of inertia and mass. Its usefulness spans a variety of fields from engineering to sports and astronomy, demonstrating its widespread importance in understanding and predicting rotational behavior.