A Closer Look at Pulse Amplitude Modulation and its Uses
Introduction
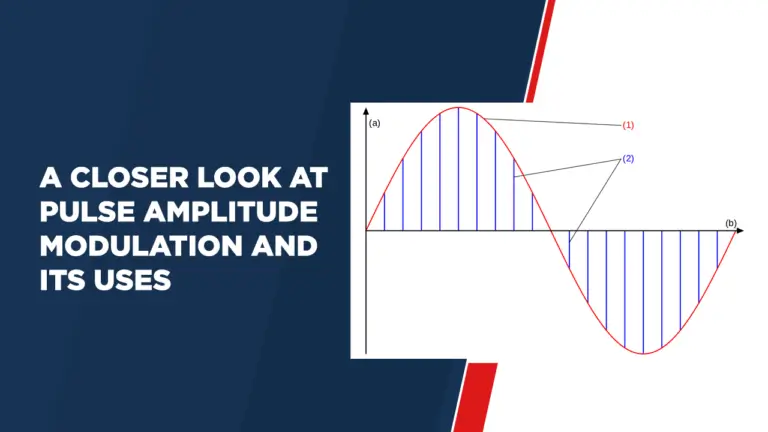
Pulse amplitude modulation (PAM), one of the more prominent modulation techniques used in communications and signal processing, plays an integral role in transmitting information quickly and reliably. PAM involves changing the amplitude of a digital pulse to carry information. This article introduces this topic in more depth including its definition, formula and various applications in the domain.
Amplitude Modulation Definition
Amplitude modulation (AM) is a modulation technique that changes the amplitude of a carrier signal according to variations in the amplitude of its modulating signal. However, with pulse amplitude modulation (PAM), individual pulses composed of digital data represent its information content by changing their individual amplitudes accordingly.
What is the Amplitude Modulation Formula?
Pulse Amplitude Modulation (PAM) can be defined as the mathematical relationship between the carrier signal and the modulating signal, which can be represented as follows:
PAM (t) = (Ac + Am ⋅ m(t)) ⋅ p(t)
Where:
PAM(t) is the modulated signal at time
Ac is the amplitude of the carrier signal,
Am is the peak amplitude deviation of the modulating signal,
m(t) represents the modulating signal as a function of time,
p(t) is the pulse waveform.
Amplitude Modulation Applications
- Telecommunications:
PAM can be used to transmit digital data over long distances by varying the amplitude of the pulse to encode multiple bits in a single pulse train – making PAM ideal for high-speed data transmission.
2. Medical Imaging:
PAM is used in medical imaging techniques such as pulse amplitude Doppler ultrasound. By analyzing the returned ultrasound pulse, health care professionals gain valuable information into blood flow and tissue properties.
3. Audio Transmission:
Amplitude modulation was historically employed in analog radio broadcasting to transmit audio signals, although more modern techniques have largely replaced this practice. Nevertheless, many aspects of AM and PAM still affect various aspects of transmission and signal processing.
4. Optical Communication:
PAM technology has also found use in optical communication systems, where variations in light pulse amplitude are used to transmit digital information over optical fiber networks at high speed and bandwidth speeds. This enables high-speed and wideband data transmission capabilities.
Conclusion
Pulse Amplitude Modulation (PAM) is an adaptable modulation technique with wide applications in various fields. By manipulating discrete pulse amplitudes, PAM provides efficient transmission of digital information. PAM has a wide range of applications from telecom to medical imaging and other fields – thus emphasizing its importance in modern communications and technology. Understanding the principles of PAM and its formula provides insight into its role in shaping how information is transmitted and received in our interconnected society.