Ohm’s Law Demystified: Empower Your Electrical Understanding Like Never Before
Introduction
In the field of electrical circuits, there exists a fundamental principle that governs the behavior of current, voltage, and resistance. This principle, known as Ohm’s law, is a cornerstone concept in the field of electronics. Ohm’s law provides a simple and elegant way to understand and predict the behavior of these essential electrical parameters. In this article, we will look at the definition of Ohm’s law, its formula, limitations, derivation and even visualize its characteristics through graphs.
Ohm’s Law Definition
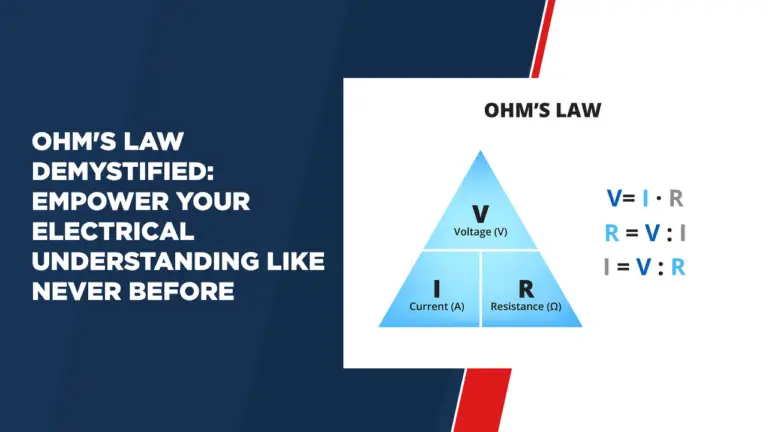
Ohm’s law is a fundamental principle in electronics that establishes a direct relationship between voltage, current, and resistance in an electrical circuit. Simply put, it states that the current passing through a conductor is directly proportional to the voltage applied across it, while inversely proportional to the resistance of the conductor. Mathematically, Ohm’s law can be expressed as:
I = V / R
Where:
– I represents the current flowing through the conductor (measured in amperes)
– V represents the voltage applied across the conductor (measured in volts)
– R represents the resistance of the conductor (measured in ohms)
Ohm’s Law Formula
Ohm’s law formula, I = V/R, serves as the basis for countless calculations in the field of electronics. Whether it is determining the current that can flow through a resistor, the resistance required to obtain a desired current at a given voltage, or the voltage required to drive a certain current through a resistor, Ohm’s law provides a simple yet powerful tool for engineers and hobbyists alike.
Limitations of Ohm’s Law
While Ohm’s law is an invaluable tool for understanding basic electrical circuits, it has its limitations. It assumes that the resistance of a conductor remains constant over a wide range of voltages and currents. However, in some cases, the resistance of a component may change due to factors such as temperature variations or other non-ideal characteristics. Additionally, Ohm’s law is not true for all types of materials, especially materials with non-linear electrical characteristics.
Derivation of Ohm’s Law
The derivation of Ohm’s law lies in the study of basic electrical circuits and the relationships between voltage, current and resistance. By analyzing the behavior of electrons flowing through a conductor, it is possible to mathematically derive the proportional relationship between these parameters. The derivation incorporates principles from both classical physics and advanced mathematical techniques, making it a fascinating exploration of electrical theory.
Ohm’s Law Graph
Visualizing Ohm’s law through a graph helps solidify the understanding of the relationships between voltage, current, and resistance. When plotted on a graph, the relationship between voltage and current for a linear resistor is a straight line. The slope of this line represents the resistance of the component. This graphical representation makes it easy to see how changes in voltage or resistance affect current flow, and vice versa.
Conclusion
Ohm’s law stands as a cornerstone principle in the field of electronics, providing a clear and concise understanding of the relationships between voltage, current, and resistance in electrical circuits. Its formula serves as a fundamental tool for engineers, students, and enthusiasts, enabling them to predict and analyze circuit behavior. While Ohm’s law has its limitations, its derivation and graphical representation further enhance our understanding of its implications. As technology continues to evolve, the timeless principles of Ohm’s Law remain an important part of the foundation upon which modern electronics are built.