Nature’s Sour Symphony: Exploring the Enigma of Acid Rain
Introduction:
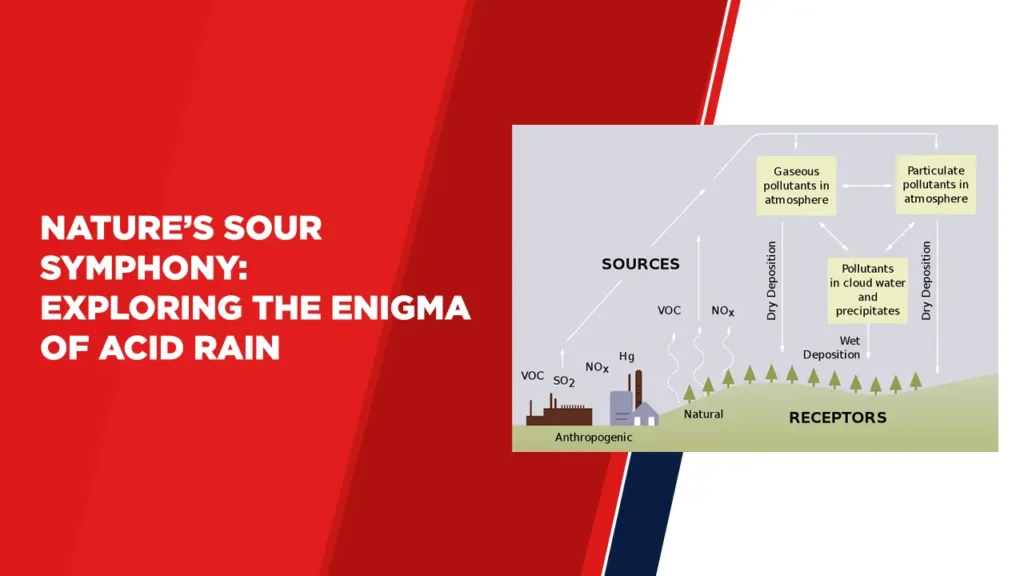
Acid rain, a concerning issue, has attracted attention due to its extensive impact on ecosystems, infrastructure and human well being. It is a result of activities such as the emission of Sulphur dioxide (SO2) and nitrogen oxides (NOx) into the atmosphere through industrial processes and transportation. When these pollutants interact with water vapor in the atmosphere they form acids that eventually descend as rain, onto the Earth’s surface.
The environmental impact of rain is widespread. Affects various ecosystems:
1. Ecosystems:
Acid rain has an effect on rivers, lakes and other bodies of water. When it mixes with the water it reduces the pH levels making it more acidic. This harms organisms like fish, amphibians and insects disrupting the food chain and reducing biodiversity.
2. Soil Degradation:
Acid rain washes away nutrients from the soil impacting the health and growth of plants. It can also release elements like aluminum into the soil further impeding plant development.
3. Forests and Vegetation:
Acid rain causes damage to leaves, disrupts photosynthesis processes and weakens trees. This makes them more vulnerable to diseases, pests and harsh weather conditions. Consequently forests in regions have been experiencing a decline.
Impact on Human Health:
While acid rain’s direct impact on human health is relatively limited, it indirectly affects humans through its consequences on the environment. The contamination of water bodies and soil can have repercussions on the safety of drinking water and food supplies, potentially exposing humans to harmful substances.
Global Concerns and International Efforts:
Acid rain is not confined to specific regions; its effects can be observed on a global scale. Countries worldwide have recognized the need to address this issue through international cooperation and policy initiatives. For instance, the United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE) has implemented the Convention on Long-range Transboundary Air Pollution to mitigate the cross-border transport of air pollutants that contribute to acid rain.
Mitigation and Solutions:
Efforts to combat acid rain have primarily focused on reducing the emission of sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides:
Regulation and Emission Controls:
Many countries have implemented strict regulations on industrial emissions and vehicle exhaust to limit the release of Sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxides.
Cleaner Technologies:
Advancements in technology have facilitated the development of cleaner energy sources and industrial processes, resulting in lower emissions.
Alternative Transportation:
Encouraging the use of public transportation, electric vehicles, and biking can reduce the emission of pollutants that contribute to acid rain.
Conclusion:
Acid rain serves as a poignant reminder of the interconnectedness of the natural world and human activities. Its environmental repercussions extend beyond national borders, necessitating global cooperation to address its root causes. By adopting sustainable practices, embracing cleaner technologies, and engaging in collaborative efforts, we can mitigate the effects of acid rain and safeguard the health of our ecosystems, ensuring a more sustainable and harmonious coexistence between humanity and the environment.