Empowering Discoveries: Harnessing the Law of Conservation of Energy to Revolutionize the Way We Live
Introduction
The law of conservation of energy is one of the fundamental pillars of modern physics. This law, based on the principle of conservation, emphasizes that energy can neither be created nor destroyed; It can only change form from one state to another. In this article, we will learn in detail about the essence of law, its derivation and its applications in the real world.
Exploring the Law of Conservation of Energy
What is the Law of Conservation of Energy?
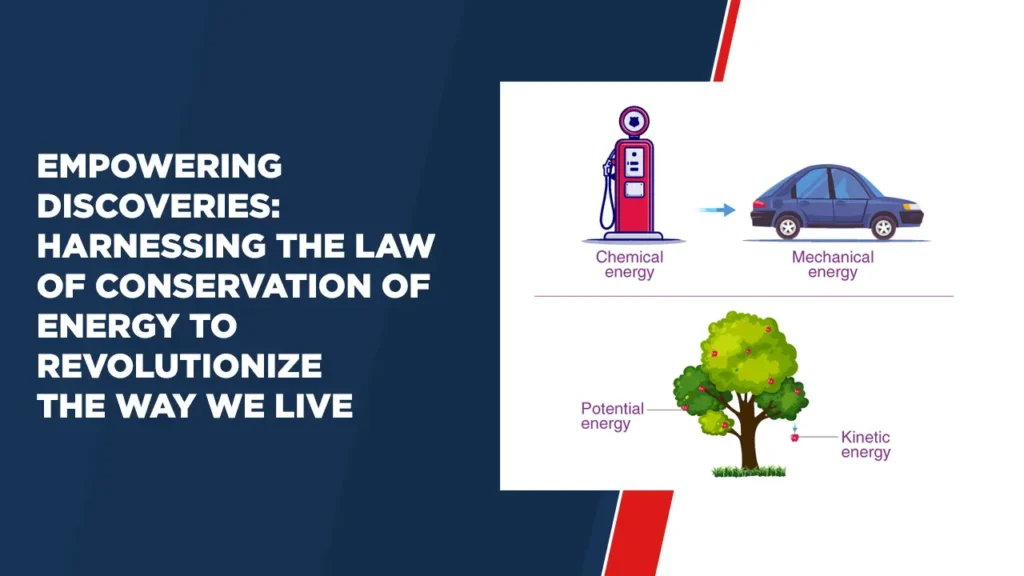
The law of conservation of energy, often called the first law of thermodynamics, states that the total energy of an isolated system remains constant over time. In simple words, energy cannot disappear into thin air or suddenly appear from nowhere; It is preserved and transformed within a closed system.
Derivation and Proof of the Law
The derivation of the law of conservation of energy involves understanding the interactions between different energy forms. Consider an isolated system where only conservative forces (such as gravity) act. By analyzing the work done by these forces and the changes in potential and kinetic energy, we can prove mathematically that the total energy remains unchanged. This derivation essentially equates the initial and final energies of the system, leading to the conclusion that energy is conserved.
Illustrating with an Example
Let us take a simple example to understand the concept better. Consider a pendulum in motion. At its highest point, it has gravitational potential energy. As the pendulum swings downwards, this potential energy is converted into kinetic energy. At the lowest point, where the kinetic energy is at its peak, the potential energy is minimum. Throughout its motion, the sum of kinetic and potential energy remains constant according to the law of conservation of energy.
Real-World Applications
The law of conservation of energy applies to a variety of fields from everyday life to advanced scientific endeavors:
- Mechanical System:
It controls the operation of machines and engines, ensuring energy efficiency and proper functioning.
2. Thermal Dynamics:
In thermodynamics, the laws underlie the concept of heat transfer and work, which enables the design of efficient heat engines.
3. Renewable Energy:
The law guides the principles of energy conversion in solar cells, wind turbines and hydroelectric dams to ensure maximum use of natural resources.
4. Chemical Reactions:
In chemistry, laws help predict energy changes during chemical reactions, aiding the development of new materials and processes.
Conclusion
The law of conservation of energy serves as a cornerstone of physics, providing a fundamental understanding of energy interactions within closed systems. Its derivation from fundamental principles and its application in diverse fields emphasize its importance in explaining the behavior of the natural world. As technology advances and our understanding deepens, this law remains a guiding principle in opening new frontiers of knowledge and innovation.