Diffusion and osmosis are fundamental processes that facilitate the movement of molecules in biological systems. While both involve the movement of substances, they differ in their mechanisms, requirements, and specific roles within living organisms. Understanding these differences is crucial for comprehending various biological and chemical phenomena.
What is Diffusion?
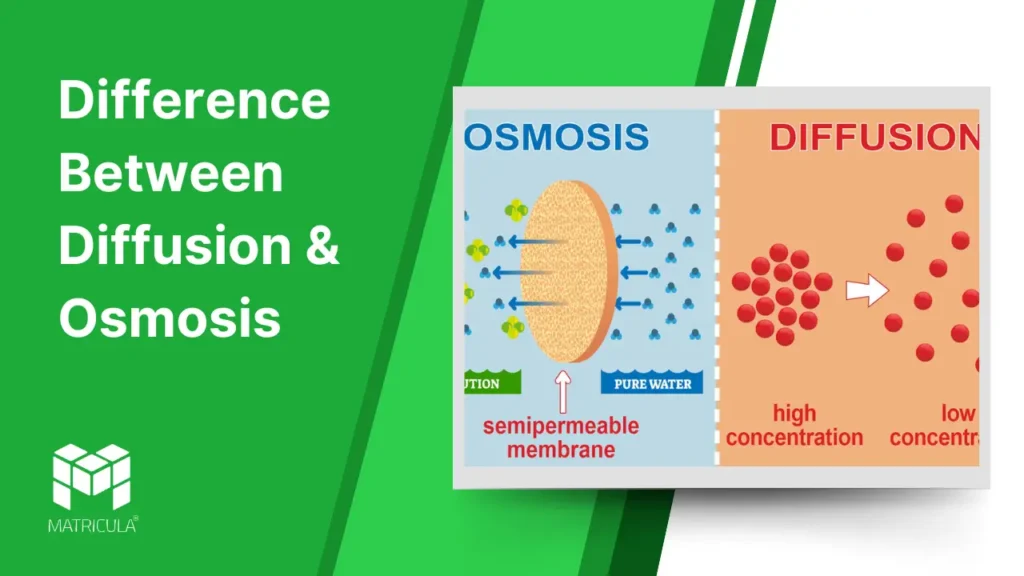
Diffusion is the process by which molecules move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration until equilibrium is reached. This process occurs due to the random motion of particles and does not require energy input.
Key Characteristics:
Can occur in gases, liquids, or solids.
- Does not require a semipermeable membrane.
- Driven by the concentration gradient.
Examples:
- The diffusion of oxygen and carbon dioxide across cell membranes during respiration.
- The dispersion of perfume molecules in the air.
Importance in Biology:
- Enables the exchange of gases in the lungs and tissues.
- Facilitates the distribution of nutrients and removal of waste products in cells.
What is Osmosis?
Osmosis is the movement of water molecules through a semipermeable membrane from an area of lower solute concentration to an area of higher solute concentration. It aims to balance solute concentrations on both sides of the membrane.
Key Characteristics:
- Specific to water molecules.
- Requires a semipermeable membrane.
- Driven by differences in solute concentration.
Examples:
- Absorption of water by plant roots from the soil.
- Water movement into red blood cells placed in a hypotonic solution.
Importance in Biology:
- Maintains cell turgor pressure in plants.
- Regulates fluid balance in animal cells.
Key Differences Between Diffusion and Osmosis
| Aspect | Diffusion | Osmosis |
| Definition | Movement of molecules from high to low concentration. | Movement of water across a semipermeable membrane from low to high solute concentration. |
| Medium | Occurs in gases, liquids, and solids. | Occurs only in liquids. |
| Membrane Requirement | Does not require a membrane. | Requires a semipermeable membrane. |
| Molecules Involved | Involves all types of molecules. | Specific to water molecules. |
| Driving Force | Concentration gradient. | Solute concentration difference. |
| Examples | Exchange of gases in the lungs. | Absorption of water by plant roots. |
Similarities Between Diffusion and Osmosis
Despite their differences, diffusion and osmosis share several similarities:
- Both are passive processes, requiring no energy input.
- Both aim to achieve equilibrium in concentration.
- Both involve the movement of molecules driven by natural gradients.
Applications and Significance
- In Plants:
- Osmosis helps plants absorb water and maintain structural integrity through turgor pressure.
- Diffusion facilitates gas exchange during photosynthesis and respiration.
- In Animals:
- Osmosis regulates hydration levels and prevents cell bursting or shrinking.
- Diffusion ensures efficient oxygen delivery and carbon dioxide removal in tissues.
- In Everyday Life:
- Water purification systems often use osmotic principles.
- Diffusion explains the spread of substances like pollutants in the environment.