From Gasps to Gases: The Astonishing Boyle’s Law Explained
Introduction
While science is full of fascinating theories that explain how matter and energy behave in our universe, Boyle’s law stands out as an iconic principle in gas physics, providing insight into the relationship between pressure and volume in confined spaces. does. In this article, we’ll delve deeper by uncovering the formula of Boyle’s law, exploring its applications through examples, and understanding its graphic representation.
What is Boyle’s Law?
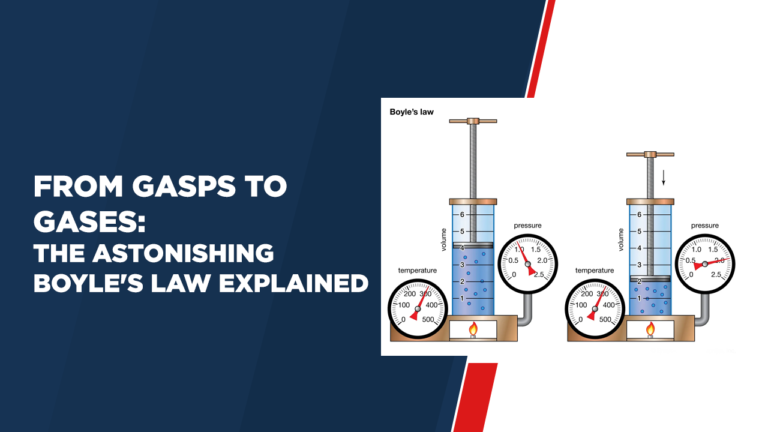
Boyle’s law, named after the Irish scientist Robert Boyle, states that when the temperature and volume of a gas are constant, its pressure and volume are directly proportional—in other words, as the volume increases , its pressure decreases, vice versa. Mathematically this rule can be expressed using this formula:
P1V1=P2V2
Where P1 and V1 represent the initial pressure and volume, and P2 and V2 denote the final pressure and volume.
Boyle’s Law Equation
This equation perfectly summarizes Boyle’s law: as the volume of a gas decreases, the particles move closer to each other—thereby increasing the pressure; Conversely, as its volume increases, there is more space between the particles, causing less pressure on them and thus a lower level.
Boyle’s Law Graph
A graph can help to show this inverse relationship. On an x-axis graph with pressure (P) as one variable and volume (V) on the other (y-axis and x-axis, respectively), there should be an inverted triangle that goes down from left to right as the volume increases. slopes down (and consequently the pressure drops), forming an “inverse hyperbola”.
Boyle’s Law Example
Imagine filling a syringe with a set amount of gas and initially expanding it completely so that the particles have enough room to move around freely. By slowly pushing back the plunger to reduce the volume of gas inside the syringe, we see Boyle’s law come into play – when the volume decreases, the pressure increases.
Conclusion
Boyle’s law is an essential concept in gas physics that describes the delicate balance between pressure and volume in a closed environment. Through its formulae, graphic representation and practical examples, we gain an in-depth knowledge of how gases react to changes in their surroundings. So the next time you hear a sigh of wonder in any walk of life, remember Boyle’s Law – the scientific principle that helps turn them into a deeper understanding of gases!