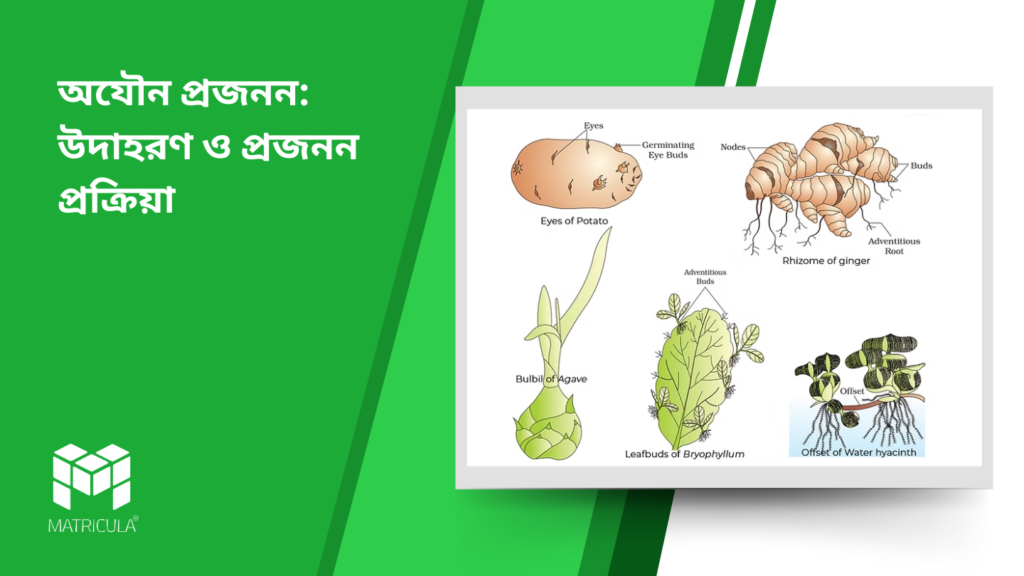
Introduction
Reproduction is a fundamental biological process through which organisms produce offspring. It is broadly categorized into sexual and asexual reproduction. In asexual reproduction, a single parent gives rise to genetically identical offspring without the involvement of gametes. This mode of reproduction is commonly observed in unicellular organisms, lower plants, and simple animals.
Asexual reproduction ensures rapid multiplication, allowing species to survive in stable environments. Several organisms use different methods of asexual reproduction, including fission, budding, fragmentation, spore formation, and regeneration. Let’s explore these processes in detail.
Types of Asexual Reproduction
1. Fission
Definition: Fission is a type of asexual reproduction in which a single organism divides into two or more new individuals. This process occurs in unicellular organisms such as bacteria and protozoa.
Types of Fission:
- Binary Fission: The parent cell divides into two equal parts, each growing into a new organism. Example: Amoeba, Paramecium, Euglena.
- Multiple Fission: The parent cell divides into many daughter cells simultaneously. Example: Plasmodium (malaria-causing parasite).
Process of Binary Fission in Amoeba:
- The nucleus of the Amoeba undergoes mitotic division.
- The cytoplasm divides, forming two daughter cells.
- Each daughter cell grows into an independent Amoeba.
2. Budding
Definition: In budding, a small outgrowth called a bud develops on the parent body, which later detaches to form a new individual. This method is common in organisms like Hydra and yeast.
Process of Budding in Hydra:
- A bud develops on the parent body due to repeated cell division.
- The bud enlarges and forms tentacle-like structures.
- After reaching a certain size, it detaches and becomes an independent Hydra.
3. Fragmentation
Definition: Fragmentation is the process where the parent body breaks into two or more fragments, and each fragment grows into a new individual. This mode of reproduction is seen in multicellular organisms like Spirogyra (a filamentous green algae) and some flatworms.
Process of Fragmentation in Spirogyra:
- The filament of Spirogyra breaks into smaller fragments due to mechanical disturbance or natural causes.
- Each fragment undergoes cell division and elongation.
- New filaments are formed, completing the reproduction process.
4. Spore Formation (Sporulation)
Definition: Some organisms reproduce by forming specialized reproductive cells called spores. These spores are lightweight, resistant to unfavorable conditions, and can disperse through air and water. This method is common in fungi (Rhizopus), mosses, and ferns.
Process of Spore Formation in Rhizopus (Bread Mold):
- The fungus develops specialized structures called sporangia.
- Inside the sporangia, numerous spores are produced through mitosis.
- When mature, the sporangium bursts, releasing spores.
- The spores land on suitable surfaces, germinate, and develop into new fungal colonies.
5. Regeneration
Definition: Regeneration is the ability of an organism to regrow lost or damaged body parts. In some cases, entire organisms can regenerate from a small body fragment. This process is seen in organisms like Planaria (a flatworm), starfish, and lizards (tail regeneration).
Process of Regeneration in Planaria:
- If a Planaria is cut into two or more pieces, each piece retains the ability to regenerate into a complete organism.
- Specialized cells divide and differentiate to restore lost structures.
- A fully functional Planaria develops from each segment.
Asexual reproduction allows organisms to reproduce rapidly and efficiently, ensuring survival in favorable environments. Different types of asexual reproduction—fission, budding, fragmentation, spore formation, and regeneration—play crucial roles in the propagation of various species. Understanding these methods helps us appreciate nature’s diverse reproductive strategies and their significance in biological processes.
অযৌন প্রজনন: উদাহরণ ও প্রজনন প্রক্রিয়া
ভূমিকা
প্রজনন হল এক গুরুত্বপূর্ণ জৈব প্রক্রিয়া যার মাধ্যমে জীবগুলি নতুন প্রজন্মের সৃষ্টি করে। এটি প্রধানত দুই প্রকার—যৌন ও অযৌন প্রজনন।
অযৌন প্রজননে, একটি মাত্র জীব অভিন্ন (জেনেটিক্যালি একই) সন্তানের জন্ম দেয়, যেখানে কোন যৌন কোষ বা গ্যামেটের প্রয়োজন হয় না। এই প্রক্রিয়াটি প্রধানত এককোষী প্রাণী, নিম্ন শ্রেণীর উদ্ভিদ এবং সহজ গঠনের প্রাণীদের মধ্যে দেখা যায়।
অযৌন প্রজননের ফলে জীব দ্রুত সংখ্যাবৃদ্ধি করতে পারে এবং এটি স্থিতিশীল পরিবেশে বেঁচে থাকার জন্য বিশেষভাবে উপযোগী। অযৌন প্রজননের বিভিন্ন পদ্ধতি রয়েছে, যেমন—বিভাজন, মুকুলন, খণ্ডন, স্পোর গঠন, ও পুনর্জনন। এবার আমরা এই প্রক্রিয়াগুলি বিশদে জানব।
অযৌন প্রজননের ধরনসমূহ
১. বিভাজন (Fission)
সংজ্ঞা: বিভাজন হল এমন একটি প্রজনন পদ্ধতি, যেখানে একটি জীব নিজেকে দুটি বা তার অধিক নতুন জীবের মধ্যে বিভক্ত করে। এটি সাধারণত ব্যাকটেরিয়া ও এককোষী প্রাণীদের মধ্যে দেখা যায়।
বিভাজনের প্রকারভেদ:
- দ্বি-বিভাজন (Binary Fission): প্যারেন্ট কোষটি সমান দুই ভাগে বিভক্ত হয়, যা পরে পৃথক দুটি জীব হিসাবে বৃদ্ধি পায়। উদাহরণ: অ্যামিবা, প্যারামেসিয়াম, ইউগ্লিনা।
- বহুবিভাজন (Multiple Fission): একক প্যারেন্ট কোষ একসঙ্গে অনেকগুলি নতুন কোষে বিভক্ত হয়। উদাহরণ: প্লাজমোডিয়াম (ম্যালেরিয়া পরজীবী)।
অ্যামিবার দ্বি-বিভাজন প্রক্রিয়া:
- প্রথমে অ্যামিবার নিউক্লিয়াস মাইটোসিস বিভাজনের মাধ্যমে দুটি অংশে বিভক্ত হয়।
- এরপর সাইটোপ্লাজম বিভক্ত হয়ে দুটি পৃথক কোষ গঠন করে।
- প্রতিটি নতুন কোষ স্বতন্ত্র অ্যামিবা হিসাবে বৃদ্ধি পায়।
২. মুকুলন (Budding)
সংজ্ঞা: মুকুলনের ক্ষেত্রে, প্যারেন্ট দেহ থেকে একটি ছোট গুটির মতো অংশ (মুকুল) গজিয়ে ওঠে এবং পরে এটি পৃথক হয়ে নতুন জীব হিসাবে পরিণত হয়। এটি ইস্ট (Yeast) ও হাইড্রা (Hydra)-তে দেখা যায়।
হাইড্রার মুকুলন প্রক্রিয়া:
- প্যারেন্ট দেহের এক অংশে ক্রমাগত কোষ বিভাজনের মাধ্যমে একটি মুকুল গঠিত হয়।
- মুকুলটি ধীরে ধীরে বড় হয় এবং এতে শুঁড়ের মতো অঙ্গ গঠিত হয়।
- সম্পূর্ণরূপে পরিণত হলে এটি প্যারেন্ট থেকে বিচ্ছিন্ন হয়ে স্বাধীন হাইড্রা হিসাবে বৃদ্ধি পায়।
৩. খণ্ডন (Fragmentation)
সংজ্ঞা: খণ্ডন হল এমন এক প্রক্রিয়া, যেখানে জীবদেহের অংশ বিশেষ পৃথক হয়ে নতুন জীব হিসাবে বৃদ্ধি পায়। এটি সাধারণত স্পাইরোগাইরা (Spirogyra)-র মতো শৈবাল ও কিছু প্ল্যাটিওহেলমিন্থ (Flatworm)-এ দেখা যায়।
স্পাইরোগাইরার খণ্ডন প্রক্রিয়া:
- স্পাইরোগাইরার ফিলামেন্ট (সুতার মতো গঠন) কোনো কারণে ভেঙে গেলে প্রতিটি খণ্ড নতুনভাবে বৃদ্ধি পেতে শুরু করে।
- প্রতিটি খণ্ড কোষ বিভাজনের মাধ্যমে প্রসারিত হয়।
- অবশেষে প্রতিটি খণ্ড একটি সম্পূর্ণ নতুন স্পাইরোগাইরা গঠিত করে।
৪. স্পোর গঠন (Spore Formation)
সংজ্ঞা: কিছু জীব স্পোর নামে বিশেষ পুনরুত্পাদনকারী কোষ তৈরি করে, যা প্রতিকূল পরিবেশেও দীর্ঘ সময় টিকে থাকতে পারে। স্পোর হালকা হওয়ায় বাতাস ও জলের মাধ্যমে ছড়িয়ে পড়তে পারে। এটি ফাঙ্গাস (Rhizopus), মস (Moss) ও ফার্ন (Fern)-এ দেখা যায়।
রাইজোপাসের (Rhizopus) স্পোর গঠনের প্রক্রিয়া:
- ফাঙ্গাস দেহে বিশেষ স্পোরাঙ্গিয়া (sporangia) নামক গঠন তৈরি হয়।
- স্পোরাঙ্গিয়ার অভ্যন্তরে মাইটোসিস বিভাজনের মাধ্যমে অনেকগুলি স্পোর গঠিত হয়।
- স্পোরগুলি পরিপক্ব হলে স্পোরাঙ্গিয়া ফেটে যায় এবং বাতাসে ছড়িয়ে পড়ে।
- অনুকূল পরিবেশে পড়লে স্পোরগুলি অঙ্কুরিত হয়ে নতুন ফাঙ্গাসের জন্ম দেয়।
৫. পুনর্জনন (Regeneration)
সংজ্ঞা: পুনর্জনন হল এমন একটি প্রক্রিয়া, যেখানে কোনো জীবদেহের বিচ্ছিন্ন অংশ আবার গঠিত হয়ে সম্পূর্ণ নতুন জীব তৈরি করতে পারে। এটি প্লানারিয়া (Planaria), স্টারফিশ ও কিছু সরীসৃপের (যেমন টিকটিকির লেজ) মধ্যে দেখা যায়।
প্লানারিয়ার পুনর্জনন প্রক্রিয়া:
- প্লানারিয়ার দেহকে যদি দুই বা ততোধিক অংশে কেটে ফেলা হয়, তাহলে প্রতিটি অংশ থেকে একটি সম্পূর্ণ নতুন প্লানারিয়া তৈরি হতে পারে।
- দেহের বিশেষ কোষ বিভাজনের মাধ্যমে নতুন অঙ্গ তৈরি করে।
- কিছু সময় পরে, প্রতিটি খণ্ড একটি পূর্ণাঙ্গ প্লানারিয়াতে পরিণত হয়।
অযৌন প্রজননের মাধ্যমে জীব দ্রুত এবং কার্যকরভাবে সংখ্যাবৃদ্ধি করতে পারে। বিভাজন, মুকুলন, খণ্ডন, স্পোর গঠন ও পুনর্জনন—এই পাঁচটি পদ্ধতি বিভিন্ন জীবের মধ্যে দেখা যায় এবং এগুলি তাদের বংশবিস্তারের জন্য অত্যন্ত গুরুত্বপূর্ণ। এই প্রক্রিয়াগুলি বোঝার মাধ্যমে আমরা প্রকৃতির বৈচিত্র্যময় প্রজনন কৌশল সম্পর্কে আরও গভীর ধারণা লাভ করতে পারি।