Aromaticity: The Allure and Chemistry of Aromatic Compounds
Introduction:
Aromatic compounds hold a special place in the realm of organic chemistry, captivating scientists with their unique properties and intriguing structures. Despite the term “aromatic” often being associated with fragrances, aromaticity in chemistry refers to a distinctive set of conjugated ring systems that exhibit remarkable stability and reactivity. This article delves into the world of aromatic compounds, elucidating their meaning, discussing aromatic amino acids, hydrocarbons, and their significance in modern chemistry.
Understanding Aromatic Compounds:
Aromatic compounds are characterised by a specific pattern of alternating single and double bonds within a closed-ring structure known as an aromatic ring. This arrangement of electrons results in enhanced stability, making these compounds less prone to reactions that would break their aromaticity.
Aromatic Meaning in Chemistry:
The term “aromatic” stems from the early observation that some of these compounds have pleasant aromas. However, the modern definition of aromaticity is rooted in the electronic structure of the compounds, specifically their resonance structures that distribute electron density evenly across the ring.
Aromatic Amino Acids:
In biochemistry, aromatic amino acids play a crucial role in protein structure and function. Phenylalanine, tyrosine, and tryptophan are three aromatic amino acids, each contributing distinct properties to proteins, including absorption of ultraviolet light and involvement in protein-ligand interactions.
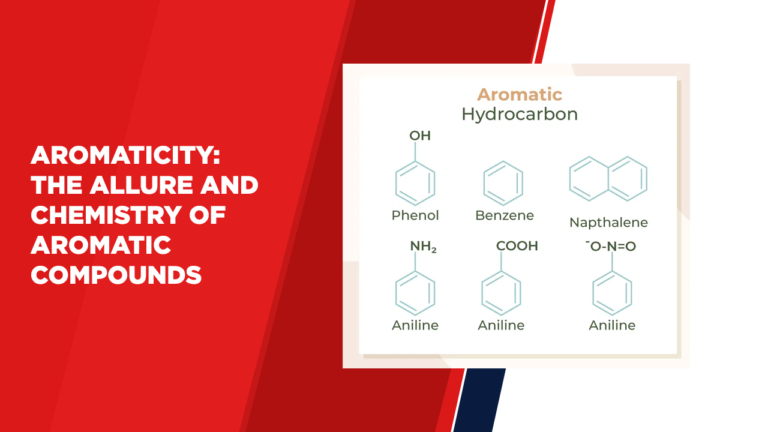
Aromatic Hydrocarbons:
Aromatic hydrocarbons are a subset of aromatic compounds that consist solely of carbon and hydrogen atoms. Benzene, the simplest aromatic hydrocarbon, is often considered the archetype of aromaticity due to its highly stable ring structure. Aromatic hydrocarbons find applications in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, polymers, and fuels.
Significance in Modern Chemistry:
Aromatic compounds are at the heart of various chemical processes and industries:
Medicinal Chemistry:
Many pharmaceuticals incorporate aromatic rings into their structures to influence their biological activity.
Material Science:
Aromatic compounds are essential components of polymers, contributing to their stability, strength, and rigidity.
Organic Synthesis:
Aromatic compounds serve as versatile building blocks for creating complex organic molecules.
Conclusion:
Aromatic compounds have stood the test of time, intriguing chemists and shaping the course of chemical research and industry. From their fascinating resonance structures to their role in biochemistry and practical applications in various fields, aromatic compounds continue to be a subject of study and innovation. As our understanding of their properties deepens, these compounds continue to inspire discoveries that pave the way for advancements in chemistry, materials science, and medicine.