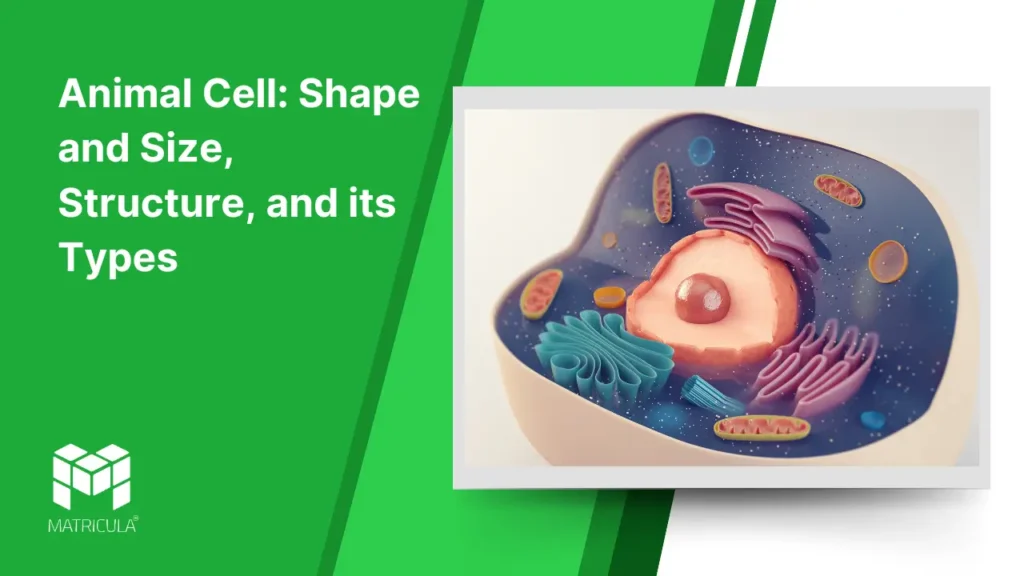
The animal cell is one of the fundamental units of life, playing a pivotal role in the biological processes of animals. It is a eukaryotic cell, meaning it possesses a well-defined nucleus enclosed within a membrane, along with various specialized organelles. Let’s explore its shape and size, structural components, and types in detail.
Shape and Size of Animal Cells
Animal cells exhibit a variety of shapes and sizes, tailored to their specific functions. Unlike plant cells, which are typically rectangular due to their rigid cell walls, animal cells are more flexible and can be spherical, oval, flat, elongated, or irregularly shaped. This flexibility is due to the absence of a rigid cell wall, allowing them to adapt to different environments and functions.
- Size: Animal cells are generally microscopic, with sizes ranging from 10 to 30 micrometers in diameter. Some specialized cells, like nerve cells (neurons), can extend over a meter in length in larger organisms.
- Shape: The shape of an animal cell often reflects its function. For example, red blood cells are biconcave to optimize oxygen transport, while neurons have long extensions to transmit signals efficiently.
Structure of Animal Cells
Animal cells are composed of several key components, each performing specific functions essential for the cell’s survival and activity. Below are the major structural elements:
Cell Membrane (Plasma Membrane):
- A semi-permeable membrane is made up of a lipid bilayer with embedded proteins.
- Regulates the entry and exit of substances, maintaining homeostasis.
Cytoplasm:
- A jelly-like substance that fills the cell, provides a medium for biochemical reactions.
- Houses the organelles and cytoskeleton.
Nucleus:
- The control center of the cell, containing genetic material (DNA) organized into chromosomes.
- Surrounded by the nuclear envelope, it regulates gene expression and cell division.
Mitochondria:
- Known as the powerhouse of the cell, mitochondria generate energy in the form of ATP through cellular respiration.
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER):
- Rough ER: Studded with ribosomes, it synthesizes proteins.
- Smooth ER: Involved in lipid synthesis and detoxification processes.
Golgi Apparatus:
- Modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids for transport.
Lysosomes:
- Contain digestive enzymes to break down waste materials and cellular debris.
Cytoskeleton:
- A network of protein fibers providing structural support and facilitating intracellular transport and cell division.
Centrioles:
- Cylindrical structures are involved in cell division, forming the spindle fibers during mitosis.
Ribosomes:
- Sites of protein synthesis, either free-floating in the cytoplasm or attached to the rough ER.
Vesicles and Vacuoles:
- Vesicles transport materials within the cell, while vacuoles store substances, though they are smaller and less prominent compared to those in plant cells.
Types of Animal Cells
Animal cells are specialized to perform various functions, leading to the existence of different types. Below are some primary examples:
Epithelial Cells:
- Form the lining of surfaces and cavities in the body, offering protection and enabling absorption and secretion.
Muscle Cells:
- Specialized for contraction, and facilitating movement. They are categorized into skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle cells.
Nerve Cells (Neurons):
- Electrical signals are transmitted throughout the body, enabling communication between different parts.
Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes):
- Transport oxygen and carbon dioxide using hemoglobin.
White Blood Cells (Leukocytes):
- Play a critical role in immune response by defending the body against infections.
Reproductive Cells (Gametes):
- Sperm cells in males and egg cells in females are involved in reproduction.
Connective Tissue Cells:
Include fibroblasts, adipocytes, and chondrocytes, contributing to structural support and storage functions.