Empowering Innovation: Semiconductors and Insulators at the Heart of Breakthroughs
Introduction
In the field of materials science, understanding the properties of conductors, insulators and semiconductors is of paramount importance. These substances form the backbone of modern electronics and play an important role in shaping our technological landscape. In this article, we highlight the differences between conductors, semiconductors, and insulators, clarifying their unique characteristics and applications.
Defining Conductors, Insulators, and Semiconductors
- Conductor:
Conductors are materials that allow the flow of electric current with minimum resistance. Metals such as copper, aluminum and gold are exemplary conductors due to their abundance of free electrons that can move freely within the material. This property makes them ideal for applications where efficient energy transfer is important, such as electrical wiring and power transmission.
2. Insulators:
On the other hand, insulators prevent the flow of electric current. They have a large energy band gap, which means that the electrons within them are tightly bound and cannot move freely. This property makes the insulator suitable for electrical insulation, preventing unwanted current leakage. Materials such as rubber, glass and plastic are commonly used insulators.
3. Semiconductors:
Semiconductors have properties that lie between those of conductors and insulators. Their energy band gap is smaller than that of insulators, which allows them to conduct electricity under certain conditions. Silicon and germanium are prime examples of semiconductors. They find wide use in electronic devices such as transistors, diodes and integrated circuits.
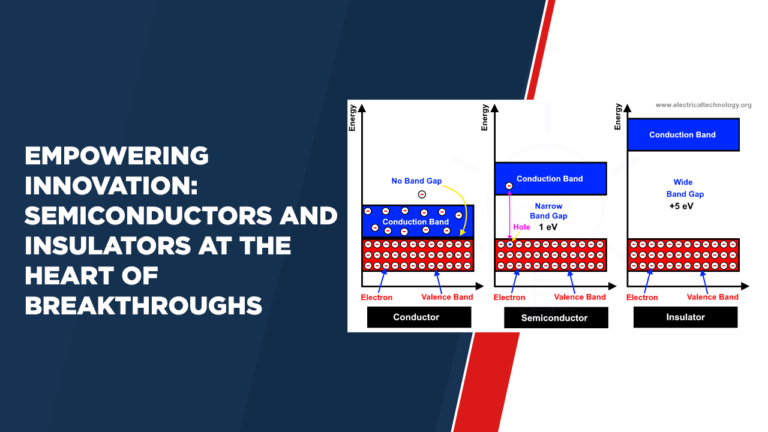
Energy Band Diagram for Conductors, Insulators, and Semiconductors
Energy band diagrams show typical characteristics of conductors, insulators, and semiconductors. In conductors, the valence and conduction bands overlap, making possible the easy movement of electrons. For insulators, a large energy difference between these bands inhibits electron movement. Semiconductors exhibit a small energy gap, allowing for controlled conductivity through the application of external factors such as temperature or impurities.
Difference between Metals, Insulators, and Semiconductors
- Conductivity:
Metals are excellent conductors due to the abundance of free electrons. Insulators have minimum conductivity due to tightly bound electrons. Semiconductors can act as either conductors or insulators depending on the external conditions.
2. Energy Band Gap:
Metals lack energy band gap, due to which their valence and conduction bands overlap. Insulators have a large energy gap, while semiconductors have a moderate gap.
3. Applications:
Metals are used in wiring and electronic equipment. Insulators are used for electrical insulation. Semiconductors are integral to microelectronics, which power devices such as smartphones and computers.
Conclusion
In the world of electronics, the distinction between conductors, insulators, and semiconductors forms the foundation of modern technology. Their diverse properties enable us to design and develop a wide range of equipment that meets our ever-evolving needs. As we continue to push the boundaries of innovation, a deeper understanding of these materials will undoubtedly fuel the progress of our technological landscape.