Understanding Reflex Action and Reflex Arc: Response and Coordination in Animals
Introduction
The ability of animals to respond swiftly to external stimuli is crucial for their survival. This response mechanism is controlled by the nervous system, ensuring coordinated movement and protective reflexes. One key aspect of this system is the reflex action and reflex arc, which enable rapid, involuntary responses to potential threats.
What is Reflex Action?
A reflex action is an automatic and immediate response of the body to a stimulus. Unlike voluntary actions, reflex actions are involuntary and occur without conscious thought. These actions are primarily defensive, protecting the body from harm.
Examples of Reflex Actions:
- Withdrawing your hand when touching a hot object.
- Blinking when an object approaches the eyes.
- Sneezing to expel irritants from the nasal passage.
Understanding the Reflex Arc
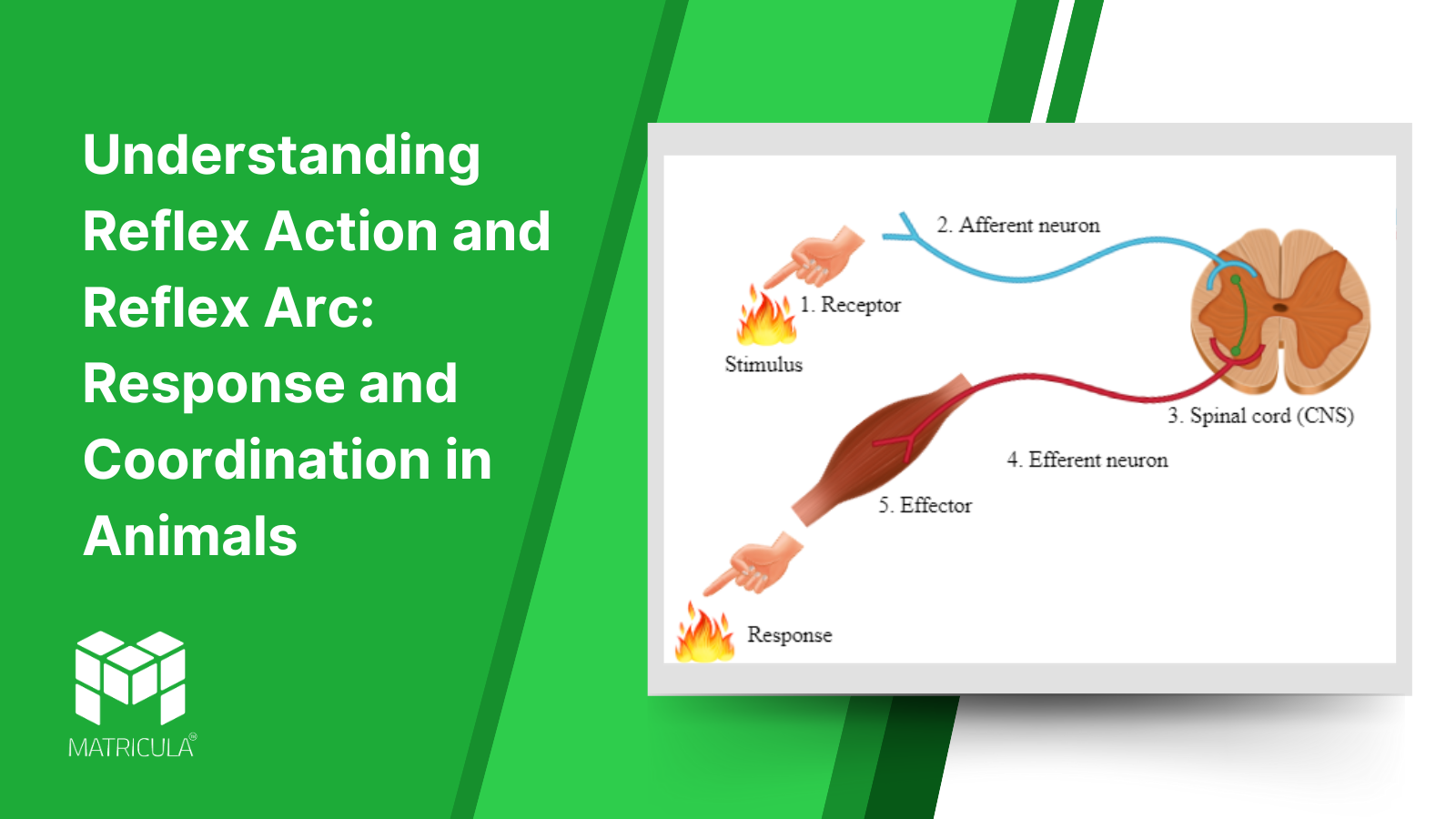
A reflex arc is the neural pathway that controls reflex actions. It allows the body to react quickly without direct involvement of the brain in the initial response.
Components of a Reflex Arc:
- Receptor: Detects the stimulus (e.g., skin receptors detecting heat).
- Sensory Neuron: Transmits the signal from the receptor to the spinal cord.
- Interneuron (Relay Neuron): Located in the spinal cord, it processes the information and sends instructions to the motor neuron.
- Motor Neuron: Carries the response signal from the spinal cord to the effector organ.
- Effector: Executes the response (e.g., muscles contracting to withdraw the hand).
How Does a Reflex Arc Work?
- Stimulus Detection: A sudden heat sensation on the skin triggers receptors.
- Signal Transmission: Sensory neurons carry this information to the spinal cord.
- Signal Processing: The interneuron processes the signal and relays a response via the motor neuron.
- Action Execution: The motor neuron activates muscles, causing an immediate withdrawal of the hand.
This bypasses conscious control to ensure a faster reaction, which is essential for avoiding potential injury.
Significance of Reflex Actions in Animals
Reflex actions play a vital role in:
- Protection: Immediate responses prevent injuries.
- Survival: Reflexes like blinking and coughing safeguard essential organs.
- Efficient Coordination: Reflex arcs enable automatic bodily functions such as breathing and digestion.
Conclusion
The reflex action and reflex arc demonstrate the body’s ability to respond swiftly and effectively to stimuli, ensuring protection and coordination. Understanding these processes is fundamental to learning about the nervous system and animal behavior. By recognizing the importance of this mechanism, students gain insights into the body’s intricate response and coordination system.