Response and Chemical Coordination in Animals: Human Endocrine Glands and Their Functions
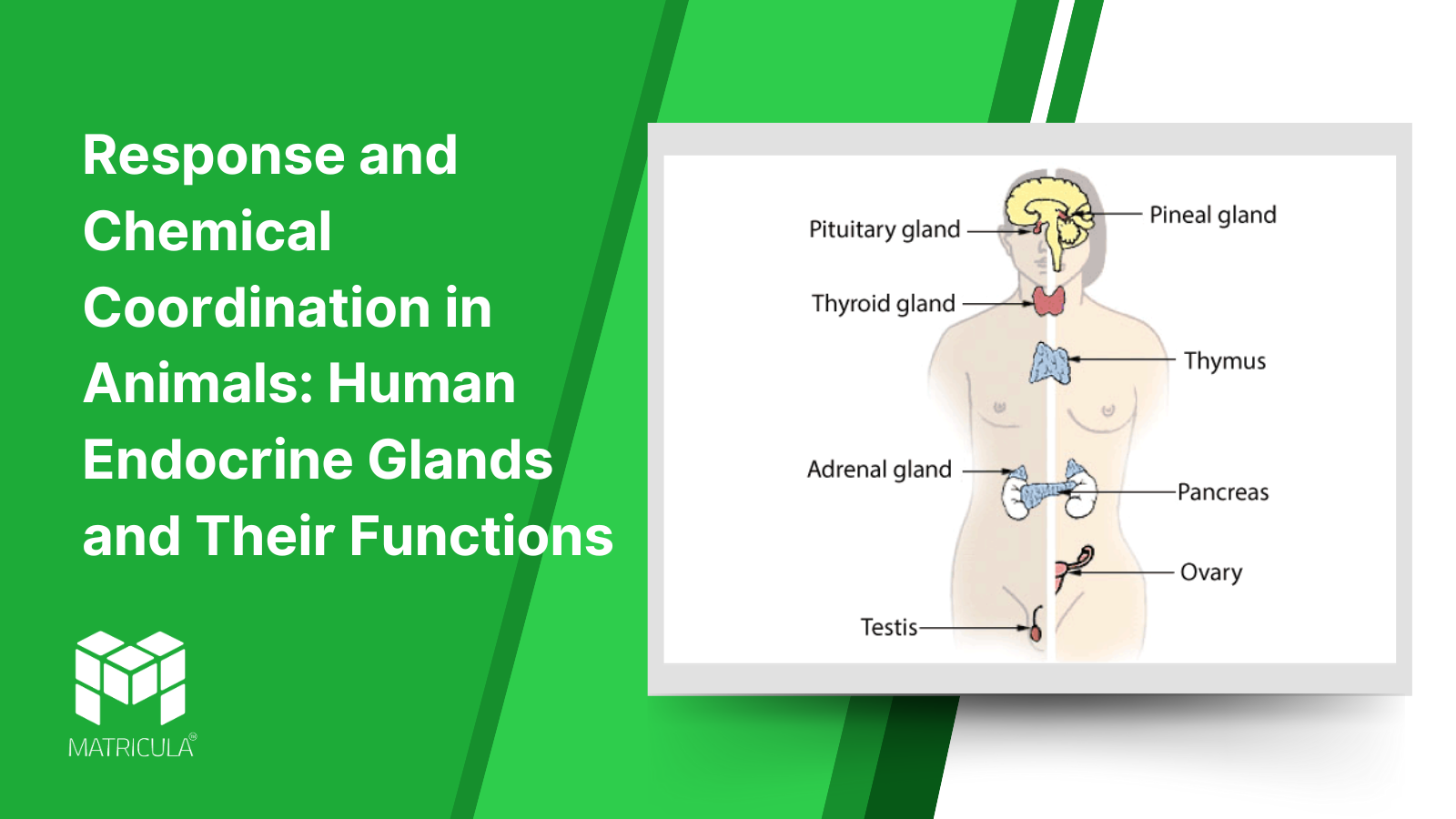
Introduction The human body relies on a complex system of chemical coordination to maintain homeostasis and ensure proper functioning. This coordination is regulated by the endocrine system, which comprises various glands that secrete hormones. These hormones play a crucial role in growth, metabolism, and overall well-being. Key endocrine glands include the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, thyroid gland, endocrine cells of the pancreas, adrenal glands, and reproductive glands.
- Hypothalamus Location: The hypothalamus is located at the base of the brain, just above the pituitary gland. It connects the nervous system to the endocrine system.
Hormones Secreted and Their Roles:
- Oxytocin: Oxytocin stimulates uterine contractions during childbirth and promotes the release of breast milk. It is also known to enhance social bonding, emotional connection, and maternal behaviors.
- Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH): ADH helps the kidneys regulate water retention by reducing water loss through urine, maintaining body hydration levels.
- Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH): TRH stimulates the pituitary gland to release TSH, which then activates the thyroid gland to regulate metabolism.
- Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH): GnRH controls the release of FSH and LH, which are crucial for reproductive processes.
- Corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH): CRH triggers the release of ACTH from the pituitary gland, helping the body respond to stress.
- Growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH): GHRH stimulates the secretion of GH, essential for growth, muscle development, and metabolism.
- Pituitary Gland Location: The pituitary gland is a pea-sized gland located just below the hypothalamus in the brain.
Hormones Secreted and Their Roles:
- Growth Hormone (GH): GH plays a key role in growth and development, promoting cell division, muscle growth, and bone density. It also influences fat metabolism and helps maintain blood glucose levels.
- Prolactin (PRL): PRL stimulates milk production in females after childbirth and influences reproductive health.
- Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH): ACTH stimulates the adrenal glands to produce cortisol, which helps manage stress, regulate metabolism, and control inflammation.
- Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH): TSH activates the thyroid gland, prompting it to release T3 and T4 hormones that regulate metabolism, energy production, and body temperature.
- Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH): FSH controls the production of eggs in females and sperm in males, playing a vital role in reproduction.
- Luteinizing Hormone (LH): LH triggers ovulation in females and stimulates testosterone production in males.
- Melanocyte-Stimulating Hormone (MSH): MSH affects skin pigmentation and helps protect the skin from UV radiation.
- Endorphins: Endorphins act as natural pain relievers and elevate mood.
- Thyroid Gland Location: The thyroid gland is a butterfly-shaped gland located in the front of the neck, just below the Adam’s apple.
Hormones Secreted and Their Roles:
- Thyroxine (T4) and Triiodothyronine (T3): These hormones regulate the body’s metabolic rate, ensuring energy production, digestion, and brain development. They also control heart rate, muscle strength, and body temperature.
- Calcitonin: Calcitonin lowers blood calcium levels by encouraging calcium absorption into bones, preventing conditions such as osteoporosis.
- Endocrine Cells of the Pancreas Location: The pancreas is located in the abdomen, behind the stomach.
Hormones Secreted and Their Roles:
- Insulin (from beta cells): Insulin regulates blood sugar by allowing glucose to enter cells, where it is used for energy. It is crucial in preventing hyperglycemia (high blood sugar).
- Glucagon (from alpha cells): Glucagon stimulates the liver to convert stored glycogen into glucose, helping to raise blood sugar when levels are low.
- Somatostatin (from delta cells): Somatostatin regulates the secretion of insulin and glucagon, balancing blood sugar levels.
- Pancreatic Polypeptide (PP): PP helps regulate pancreatic enzyme secretion and digestive functions.
- Adrenal Glands Location: The adrenal glands are located on top of each kidney.
Hormones Secreted and Their Roles:
- Adrenaline (Epinephrine): Adrenaline prepares the body for emergencies by increasing heart rate, blood pressure, and energy release. It sharpens mental alertness during stressful situations.
- Noradrenaline (Norepinephrine): Similar to adrenaline, noradrenaline raises heart rate and blood pressure during stress.
- Cortisol: Cortisol helps manage stress, reduces inflammation, regulates metabolism, and controls blood sugar levels.
- Aldosterone: Aldosterone maintains sodium and potassium balance, ensuring proper blood pressure control and hydration.
- Androgens: These hormones influence the development of male secondary sexual characteristics, such as body hair and deepening of the voice.
- Reproductive Glands Location: The testes are located in the scrotum in males, while the ovaries are situated in the lower abdomen in females.
Hormones Secreted and Their Roles:
- Testosterone: Testosterone is crucial for the development of male reproductive organs, muscle growth, bone density, and secondary sexual traits like facial hair and voice deepening.
- Estrogen: Estrogen regulates the menstrual cycle, promotes breast development, and supports female secondary sexual characteristics.
- Progesterone: Progesterone prepares the uterus for pregnancy and maintains the uterine lining for embryo implantation.
- Inhibin: Inhibin regulates FSH secretion to control egg and sperm production.
Conclusion The human endocrine system plays a crucial role in ensuring body functions remain balanced and well-coordinated. Each gland contributes to regulating growth, development, metabolism, and overall health. Understanding these glands, their hormone functions, and their roles in bodily processes is essential for maintaining well-being. Regular check-ups, balanced nutrition, and a healthy lifestyle can significantly enhance endocrine health.